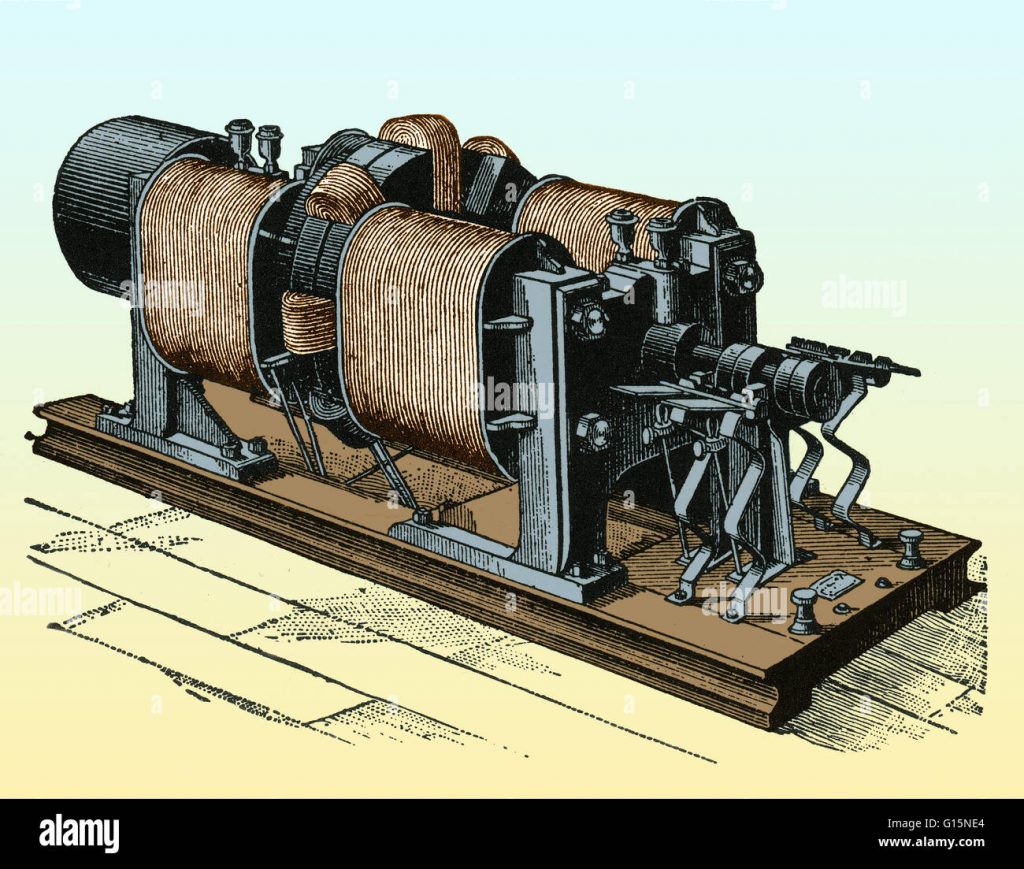
The first generator was invented in the early 19th century by the German engineer Hippolyte Pixii. It was the first device to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, and it used the principle of a rotating magnetic field. The generator was a major breakthrough in electrical engineering and paved the way for the development of modern power plants. It was able to produce an alternating current at a stable frequency, making it ideal for powering early telephones, telegraphs and light bulbs. Pixii’s generator used a hand-cranked magneto to generate an electric current, making it the first practical generator in history.
It was a relatively simple device and could be mass-produced relatively cheaply. Pixii’s generator was the first device to provide a reliable, commercially viable means of generating electrical power. It revolutionised the way electricity was produced and consumed, and enabled the development of modern electrical networks. Since then, generators have become increasingly advanced and efficient. Today’s generators are used to generate vast amounts of electricity for homes, businesses and industrial applications all over the world.
Why did cars stop using generators?
The first generators were used in cars to provide electrical power to the vehicle. This was a revolutionary advancement for the automobile industry because it allowed cars to be powered by electricity, rather than relying on gasoline. However, the technology of the first generators was not very efficient and relied heavily on the movement of the car to generate energy. As the technology of generators evolved, newer and more efficient models were developed. This allowed for more energy to be produced with less strain on the car, resulting in improved engine performance.
These newer generators were also much more reliable than their predecessors, meaning less breakdowns and fewer maintenance costs. Unfortunately, the generators were still not as efficient as other forms of power, and they still relied on the movement of the car to generate energy. This led to the eventual phase-out of generators in cars in favor of more efficient forms of power, such as batteries and fuel cells. This switch to more efficient forms of power allowed vehicles to be powered more reliably and efficiently. Cars no longer needed to constantly rely on the power generated by the generator to move, resulting in a smoother, more reliable driving experience. Overall, the switch from generators to more efficient forms of power was beneficial for the automobile industry. Generators were simply not efficient enough to be a viable long-term solution, so the switch allowed cars to be powered more reliably and efficiently.
Did old cars have generators?
The first generator was developed in the late 1800s and early 1900s. It was used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. Old cars before the mid-1900s had generators as well. They were used to provide electrical power for the ignition system, and to power the lights and other electrical components in the car. These generators were usually driven by either a belt connected to the engine, or a fan driven by the crankshaft.
They contained a rotating armature surrounded by magnets, which produced electricity when the magnets rotated. Generators in early cars were relatively simple and lasted for a long time, but they were also very inefficient and required more frequent maintenance. As cars became more sophisticated, modern alternators replaced the generators in most cars. The alternator is more efficient and reliable than the generator, and it is still used in modern cars today. However, some car enthusiasts and collectors still prefer the classic look and feel of an old car with a generator.
Who invented first generator?
The first generator was invented by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday was an English scientist who discovered the principles of electromagnetic induction, which is the basis of nearly all generators and motors today. He developed the first crude generator using a copper disk, a magnet, and a length of wire. When Faraday rotated the copper disk between the magnet’s poles, he observed that the motion of the disk caused electrical current to flow in the length of wire. This was the first generator ever created. Faraday’s generator was later improved upon by Hippolyte Pixii, who in 1832 invented the first commercial generator. Pixii’s generator was a tiny dynamo powered by a hand crank. He used it to power a light bulb, making it the world’s first electric generator. Over the years, generators have been developed to power a wide variety of products such as cars, home appliances, and tools. Generators have also been adapted to many different sources of energy such as steam, gasoline, and solar power. Today, generators are used to produce electricity in most parts of the world. Generators are essential to modern life and are largely responsible for the industrial revolution. Thanks to Michael Faraday’s ingenious invention, modern life as we know it would not exist without the generator.
What was the first generator called?
The first generator was invented in 1831 by Michael Faraday. It was called the Faraday dynamo and was the first machine to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. Prior to this invention, electricity was produced by batteries and electrostatic generators. The Faraday dynamo consisted of a loop of wire rotating between two magnets. As the wire rotated, it would induce an electrical current.
This was the first time that electrical energy was created from mechanical energy. Faraday’s invention paved the way for further developments in the field of electrical power generation. In 1866, the world’s first commercial power generator was built in London. This generator used rotating coils of copper to generate electricity. The Faraday dynamo was a major breakthrough in the history of electricity and had a huge impact in shaping the modern world. It made possible the generation of large amounts of power, which was necessary for industry, agriculture, and transport. The Faraday dynamo is still considered one of the most important inventions of the 19th century, and its legacy has been recognized throughout history. Thanks to Michael Faraday, the world today is powered by electricity.
Who invented generator in 1860?
In 1860, the first generator was invented by a man named Zenobe Gramme. He was a Belgian electrical engineer and physicist who developed the first practicable electric generator. His work was essential in the development of the modern electrical industry. The generator invented by Gramme used a commutator and electromagnets to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. It was the first device to be able to produce a continuous flow of electric current, and it revolutionized the way electricity was produced and used.
Gramme’s generator was the first to be able to generate more than one volt of electricity, and it was the basis for the generators used in today’s power plants. It was also the first device to make the large-scale production of electrical energy practical, which enabled the development of our modern electrical grids. The invention of Gramme’s generator marked the beginning of the modern electrical age. Before his invention, electricity had been used in limited ways in medical treatments and scientific experiments, but it had never been used in a way that could produce a large amount of electricity. His generator allowed scientists to explore the potential of electricity, which led to the development of numerous applications and inventions. Gramme’s generator is a testament to his genius and pioneering spirit. His invention opened the door to a future of electricity-powered technology that has changed the way we live today. Without his groundbreaking invention, the world would look very different.
Did Nikola Tesla make a generator?
Nikola Tesla is well known for his inventive genius and contributions to science. He is credited as the inventor of the first generator. This generator was revolutionary for its time, as it was constructed with alternating current rather than direct current, which made it much more efficient. Tesla spent many years developing the generator, perfecting his ideas to ensure it could be used on a larger scale. The generator used a process of induction and magnetism to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
This was a major technological breakthrough at the time, as it made it much easier to generate large amounts of electricity without the need for bulky and expensive equipment. Tesla’s first generator was a great success and was used in homes, factories and power plants around the world. It revolutionized the generation of electricity and enabled us to have access to a reliable, affordable energy source. Tesla’s invention and the resulting power revolution continues to have an impact today, as the generator still remains a mainstay of electricity generation around the world. In short, Nikola Tesla did indeed make a generator, and it was the first of its kind. His invention revolutionized the way we generate electricity and continues to have a lasting impact on modern society.
When was electricity first used in homes?
Electricity was first used in homes in the early 1800s. The first generator, invented by Michael Faraday, was used to produce electricity in 1821. It was a dynamo, which is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. At first, electricity was used for scientific purposes, but by the late 1800s, it was being used in factories. The first commercial electric power plant was built in 1882. This plant provided electricity to nearby homes and businesses. By the early 1900s, many cities had power plants that could provide electricity to homes. Electric lighting became popular, and many people began to use electric appliances in their homes. By 1930, electricity was widely used in homes all over the world. Today, most homes have electricity as a basic necessity. It powers lights, appliances, heating and cooling systems, computers and many other devices. In fact, electricity is so pervasive that it is hard to imagine life without it.
Who invented the first electric generator?
The first electric generator was invented by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday was an English scientist who demonstrated the first generator in 1831. This generator was able to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. Faraday’s invention changed the world by providing an efficient way to produce electricity. The first generator was a simple device consisting of a copper disk which was rotated between the poles of a horseshoe-shaped magnet. As the disk rotated, it induced electric current in the copper wire which was connected to it. This current was then used to power electric lamps and motors. The success of Faraday’s invention inspired other scientists, who improved upon the design of the electric generator and developed larger and more efficient versions. The modern electric generator, which is used to generate electricity for commercial and residential applications, is based on Faraday’s pioneering work. Thanks to Faraday’s invention, the modern world has access to reliable electricity. The electric generator has revolutionized industry and revolutionized the way we live our lives. It has enabled us to use electricity to power our homes, workplaces, and even our cars. Faraday’s invention has been crucial in the development of modern society and continues to be an integral part of our lives.
What are the best electric generators?
The first electric generator was a major breakthrough in the world of energy generation. It opened the door for a whole new way of providing power to homes and businesses. Today, there are many different types of electric generators available to meet a variety of needs. The best generators are those that are reliable, efficient, and cost-effective. The most popular type of generator is the portable electric generator, which is designed to provide a convenient backup power supply for homes and businesses in the event of a power outage.
These generators can be used in a variety of locations, from camping and tailgating to emergency situations. Inverter generators are another popular choice for those who need a reliable source of power. These generators are more efficient than portable generators and can provide more power with less fuel. They are also quieter, making them a great choice for camping or tailgating. For those who need to power larger appliances or equipment, a standby generator is an excellent choice. These generators are more powerful than other types of generators and are designed to provide a steady supply of electricity when the power goes out. No matter what type of generator you choose, it is important to get one that is reliable, efficient, and cost-effective. Electric generators are an invaluable source of power and can supply emergency power in any location.
Where was the first generator used?
The first generator was used in the early 1800s to produce electricity for scientific experiments. It was built by British scientist Michael Faraday and was based on the principles of electromagnetism discovered by Danish physicist Hans Christian Oersted. Faraday’s generator was the first machine to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, and marked an important milestone in the history of electricity. The generator was a simple device, consisting of two coils of insulated wire wrapped around a metal core. When the metal core was rotated, it created a magnetic field, which in turn produced an electric current in the coils.
This current was then used to power scientific experiments, such as producing sparks and electrostatic charges. Faraday’s generator was the first of its kind, paving the way for the development of more sophisticated generators. These generators eventually led to the development of dynamos, which are still found in use today. They are used in many different applications, including power plants, electric motors, and even electronics. The first generator was an important step in our understanding of electricity, and it has paved the way for the development of many technologies we use today. From small home appliances to large-scale power plants, the first generator has enabled us to take full advantage of the power of electricity.
What did Michael Faraday invent?
Michael Faraday was a renowned scientist and inventor in the 1800s. He is best known for his invention of the first generator, a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Faraday’s generator was composed of a powerful electromagnet, a wire coil, and a conducting disc. When the disc was rotated between the poles of the magnet, electricity was produced. Faraday’s invention of the first generator was a major breakthrough in the history of science.
It allowed for a much more efficient way of producing electricity, which in turn led to the development of many more electrical devices in the following decades. This invention ultimately led to the industrial revolution and the world-wide use of electricity. Faraday’s generator was the foundation of his many other inventions that revolutionized science. He was also responsible for the discovery of electromagnetic induction, which is the basis of many of today’s electric motors and generators. Michael Faraday’s legacy lives on through his inventions, which still influence the way we use electricity today. His invention of the first generator truly revolutionized the way electricity is made and used. It was a major breakthrough in the history of science, and it is a testament to Faraday’s genius.
When was the generator first invented?
The first generator was invented in 1831 by Michael Faraday, an English scientist. Faraday was the first to discover the principle of the electric generator and successfully build the first generator. His invention made it possible to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. Faraday’s generator used a copper disk that was spun between two electromagnets and the spinning disk would produce an electric current. This generator was very inefficient since it only produced a small amount of electrical energy.
Since then, the generator has evolved and improved over the years. Many advancements have been made to the design and technology of generators. Modern day generators are much more efficient and are capable of producing a large amount of electrical energy. Generators are now used in many different applications and are essential parts of our lives. They are used in homes, businesses, cars, boats, and many other places. Generators are also commonly used in industries to power machinery and provide electricity for the entire factory. Generators have come a long way since their invention and have had a major impact on our lives. Without them, our lives today would be much more difficult.
Can a generator run forever?
The first generator was invented in the early 19th century to provide an alternative to traditional energy sources. It produces electricity by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. But the question remains: can a generator run forever? The answer is no, a generator cannot run forever. Generators require fuel to operate, and running a generator over a long period of time can lead to mechanical problems or breakdowns due to wear and tear on its components. Without proper maintenance, a generator can break down and need to be replaced or repaired.
Generators have a finite lifetime based on its design and size, as well as the quality of the parts used. Heavy-duty generators can run for many years without needing major repairs. However, as with any machine, proper maintenance is essential to ensure a long life for your generator. It is important to remember that no generator can run forever without proper maintenance. Regular maintenance and replacement of worn parts will help extend the life of your generator and ensure it runs for a longer period of time. Additionally, using fuel that is designed specifically for generators can improve their efficiency and reduce the need for repairs. In conclusion, while a generator can run for a considerable amount of time, it is not able to run forever without proper maintenance and care. Therefore it is important to take care of your generator if you want it to last for a long time.
When was the first DC generator invented?
The first DC generator was invented in 1832 by Michael Faraday. It was known as the Faraday disc and was the first generator capable of producing a usable amount of electrical power. This generator was made up of a copper disc that was rotated between the poles of a magnet. As the disc rotated, it created a steady current of electricity which could then be used for a variety of purposes. The Faraday disc was later improved upon by Hippolyte Pixii, who added a commutator to the generator in 1832.
This allowed for the electricity produced by the generator to be reversed when needed. This enabled the generator to be used for different purposes, including powering electric motors. In the late 1800s, DC generators continued to be improved upon. In 1891, the first commercially successful DC generator was invented by Charles F. Brush. His generator was capable of producing high voltage and was used to power early lighting systems. Since then, DC generators have become an integral part of our lives and are used in many applications, from automobiles to home appliances. They are highly efficient and can produce a steady stream of electricity for a variety of different uses. The first DC generator was a major breakthrough and paved the way for the development of more advanced generators, which are now commonplace in our everyday lives. Without it, many of the conveniences we enjoy today would not be possible.
Which came first DC or AC?
The invention of the first generator is credited to Michael Faraday, a scientist from the 19th century. He invented a device that could convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. This machine used direct current or DC, which means the electric charges moved only in one direction. A few years later, another scientist, Nikola Tesla, improved on Faraday’s invention by introducing alternating current or AC, which means the electric charges moved back and forth. AC was a major improvement because it could transmit electricity over greater distances with less loss of power compared to DC. Both DC and AC are still used today, but AC was the first form of electrical energy to be generated by a machine. Hence, AC came before DC in the context of the first generator.
Who invented the first generator in 1832?
In 1832, the first generator was invented by Michael Faraday. This generator was powered by a rotating magnetic field and allowed the production of electricity for the first time. Faraday’s invention is still considered a major breakthrough in the history of electricity production and is the basis for all modern generators. The first generator was a primitive device, but it was able to produce enough electricity to light a lamp. It was made from a copper disk, inside of which was a magnet, and this was suspended between two poles of a horseshoe electromagnet.
When the disk was turned, the magnet rotor moved, creating an electric current. Faraday’s invention revolutionized the way that electricity was produced. It allowed the production of large amounts of electricity very quickly and cheaply, and this opened up a vast range of potential applications. It was the foundation of the modern electric power industry and led to the development of power plants and electrical grids. Today, generators are used to generate electricity for a variety of applications, from powering homes and businesses to providing energy for large industrial plants. The invention of the first generator was a major breakthrough in the history of electricity production and laid the foundations for the modern power industry.
Who first generated electricity?
The first generator was invented by Michael Faraday in 1831. He used it to generate electricity by passing a current through an electromagnet. This was the first time electricity had been generated on a large scale. Faraday’s generator was an alternating current generator, which paved the way for the development of electric motors and later electrical generators. His work was so influential that it has been termed the “Faraday effect”. Faraday was also the first to discover the principles of electromagnetic induction and to use it to generate a current. His inventions revolutionized the electrical industry and had a major impact on the development of power generation. Faraday’s electricity generator, known as the Faraday disk, was the first device that could generate electricity on a large scale. This device became the basis for modern electric generators. Faraday’s work was a major milestone in the history of electricity generation, and it enabled the development of power plants and electrical networks that are used today. Faraday’s discovery has been described as a major breakthrough in the history of electricity generation, and his work is often credited as the beginning of the modern electricity industry. His inventions were instrumental in the development of today’s electric power systems, and they helped shape the way electricity is generated and used. In conclusion, Michael Faraday is widely regarded as the first person to generate electricity on a large scale. His work revolutionized the electrical industry and had a major impact on the development of electric power generation. His inventions have shaped the way electricity is generated and used in today’s world.
When was the first generator created?
The first generator dates back to the 18th century when the first electrical generator was invented by Michael Faraday. Faraday used a copper disk to demonstrate the idea of a generator and thus created the first one. His invention used a process of induction to generate electricity. This primitive generator used a magnet to spin the copper disk and a coil of wire to capture the induced current. This current would then be used to power an electric motor.
It was an important milestone in the development of electricity, paving the way for more advanced generators. In the 19th century, more efficient generators were developed. These generators used steam engines to spin magnetic fields, which then generated electricity. This made electricity more widely available and allowed for the invention of electric lights and other modern conveniences. By the early 20th century, more efficient generators had been invented. These generators used internal combustion engines, which were more reliable and efficient. This made the use of electricity even more widespread, and allowed for the invention of the modern power grid. The first generator has come a long way since Faraday’s invention. Today, generators are an essential part of our lives, providing us with electricity and powering our homes and businesses. Without it, modern life would be completely different.
Who is the first person to create a generator in 1831?
The first person to create a generator was Joseph Henry in 1831. He was an American scientist and one of the first major researchers into electricity. He was the first to build a generator that could create electricity by turning a handle. The generator he built was based on the principles of electromagnetic induction which he had been researching since 1825. This new device was able to generate electrical power from mechanical energy. It was the first practical device for creating electricity, revolutionizing the field of electrical research. Joseph Henry’s generator had an armature and a horseshoe-shaped electromagnet. He wound the armature with wire and connected it to a battery. When the handle was turned, the armature rotated and the electromagnet generated electricity. The electricity was then sent through the connected battery. Joseph Henry’s invention marked the beginning of the modern era of electricity. His breakthrough in electrical engineering allowed for new applications and advancements in electrical power generation and transmission. His invention ushered in a new era of electrical invention and technological advancement. Joseph Henry’s invention of the first generator was a major milestone in electrical engineering and opened up new possibilities in the field. His invention has enabled us to power our homes, businesses, and cities, and it has enabled us to explore the world of electricity and technology.
Where was generator invented?
In 1831, the first generator was invented by Michael Faraday. He was an English scientist who discovered the principles of electromagnetic induction. This generator was a primitive device that used a magnet and a coiled wire to create electricity. Faraday’s generator was the first device to be able to produce a continuous flow of electrical current. The first generator was a crucial breakthrough in the field of electricity.
It allowed engineers to find new and better ways to generate and store electricity. This would eventually lead to the development of the modern electrical system. Faraday’s generator was improved upon over the years. By the end of the 19th century, generators had become much more efficient and powerful. They were capable of producing large amounts of electricity for homes and businesses. Today, generators are still widely used for many different applications. They are used to power cars, airplanes, and even spacecraft. They are also used to create electricity for homes and businesses and to provide backup power during outages. Generators have come a long way since Michael Faraday’s first generator. His invention spurred a revolution in the way we use and think about electricity, and it remains one of the most important inventions in the history of electricity.
Who first make generator?
The first generator ever made was invented by Michael Faraday in 1831. He was a scientist and an inventor who discovered the principles of electromagnetic induction, which was the basis for the first generator. Faraday’s generator was a type of rotary generator powered by a hand crank. This generator only produced a small amount of electricity but was the first to do so. Faraday’s invention was a major breakthrough for the development of future electricity generation methods. His invention was improved upon by many other inventors and engineers who developed generator designs that could produce more electricity. These improvements led to the generators we use today in our homes and businesses. Faraday’s generator was a major step forward in the development of electricity. This invention was a major breakthrough in the evolution of electricity and helped propel the industrial age. Without Faraday’s invention, we may not have the electrical devices and appliances that we rely on today. Faraday’s generator was a revolutionary invention that changed the way we use electricity. His invention was the first generator to successfully generate electricity and paved the way for future generations of electricity generators. We are still using the principles he discovered in the development of electricity production and consumption.
What is the principle behind electric generator?
The first electric generator was invented in 1831 by Michael Faraday and it was based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. This principle states that when a conductor moves through a magnetic field, a current is induced in the conductor. This current causes a force to be generated within the conductor, which generates a rotational force that can be used to drive a generator. The generator then produces electricity from this rotational force. This is a basic principle of an electric generator and it is used in all sorts of applications, from small portable generators to large power plants.
It is a simple yet powerful method for producing electrical energy, which can be used for a variety of purposes. Electric generators are used to provide electricity to homes, offices, and even large-scale industrial complexes, as well as to power all sorts of machinery. The generator creates electrical energy from the mechanical energy of the rotor, which is then converted into an alternating current. Electric generators are also used in transportation, such as in electric cars and helicopters. The principle behind electric generators has been used in all sorts of applications, from the small to the large, and is essential for modern life.